NHLBI, 2022 Fall
Welcome to the 2022 course!
This offering is for Division of Intramural (DIR), NHLBI in Fall, 2022.
Based on the feedbacks from the last offering, this time we will split the course into two parts. The first part: Deep Learning Fundamentals consists of 8 lectures. We will start from basics of neural networks, introduce the loss function, optimization and how to setup and manage the training session. The next section is the convolutional neural network for imaging and vision tasks. We will then learn the recurrent neural network (RNN) for the sequence data.
The second part: Deep learning Advances consists of 6 lectures. We will start at the attention mechanism and transformer models (BERT, GPT family etc.). In particular, the natural language processing applications using large deep learning models will be reviewed. We will then learn the generative model and in details the GAN (generative adversarial network). The technique to visualize the neural network is introduced to help understand how and why the neural network works. The course will end with a focus on how to handle "small dataset" usecase, as in many practical applications, we may not be able to acquire large labelled dataset. Three techniques are introduced, transfer learning, meta learning and contrastive learning (as the more recent development of self-supervised learning).
For the NHLBI DIR community, the teaching objectives are:
* Introduce the basics of deep learning
* Present in-math how DL model works
* Provide practices to build your own model
* Grow interest and improve community awareness
* Prepare trainees and fellows for DL related jobs
For the student point of view, you will gradually learn the concepts and algorithms behind the deep neural network and master the tools required to build and train models. For every lecture, it comes with a reading list to broaden the understanding.
We will use Pytorch. So it is a good idea to get yourself familiar with this package.
Prerequisites
Please review the mathematics for deep learning and learn basic Python and Numpy.
- mathematics for deep learning
- Python, a more comprehensive book
- Python Crash Course, one of the easiest tutorial
- Numpy
- Pytorch tutorial
- Debug python program using VSCode
Instructors
- Hui Xue, hui.xue@nih.gov
Schedule
Part 1: Starting on the week of Sep 12, 2022
-
Lecture, every Wed, 11:00am-12:30pm, US EST time
- Link to be added
-
Q&A session, every Friday, 11:00am-12:00pm, US EST time
- Link to be added
Part 2: Starting on the week of Jan 9, 2023
- Lecture, every Wed, 11:00am-12:30pm, US EST time
- Link to be added
Assignments
Three assignments will be provided for the part 1 of the course. These assignments combine the multi-choice questions and coding sampling. They are designed to help you understand the course content and practise skills to build models.
Based on the feedback collected last year, the solutions of assignments will be provided to you two weeks after the release of questions ^(). The purpose is to encourage independent work, but still limit the time effort one may spend on the questions.
Syllabus
Part 1: Deep learning fundamentals
Prologue
Why do we want to spend hours in learning deep learning (DL)? I can articulate one reason: Deep Learning is a set of key technique which can be applied to many fields, from mobile phone to medical imaging, from robotics to online shopping, from new drug discovery to genomics. What is really amazing to me is that in this wave of technological revolution, the same set of technique, deep neural network, is solving many challenging problems which are drastically different. Yes, it is the same set of algorithms, software toolboxes and knowledge base are applied, reporting state-of-the-art performance.
This makes learning deep learning rewardable, because you will master something which can be widely applied and mostly likely will stay that way in the decades to come. According to ARK's research, deep learning will add $30 trillion to the global equity market capitalization during the next 15-20 years*. No something which should be ignored!
However, there are difficulties along the way. Often, more than superficial level of understanding of DL is required, if you want to find a notch to apply DL in your field and if no one has done this before you. There will not be pre-trained models which you can download. One has to understand the problem and design the model, invent new loss functions and put all pieces together to build a DL solution. Your solution needs to prove its value in deployment and gets better over time.
This course is to equip you with required knowledge to understand and apply DL by teaching how the deep neural network models work and by reviewing many DL architectures and applications. My hope is after this learning process, domain experts will feel confident to apply DL to their specific problems and datasets.
Video
Slides
Suggested Reading
- *For big pictures and where DL can fit, Ark Big Idea
- Artificial Intelligence Index Report 2022, AI report
Lecture 1
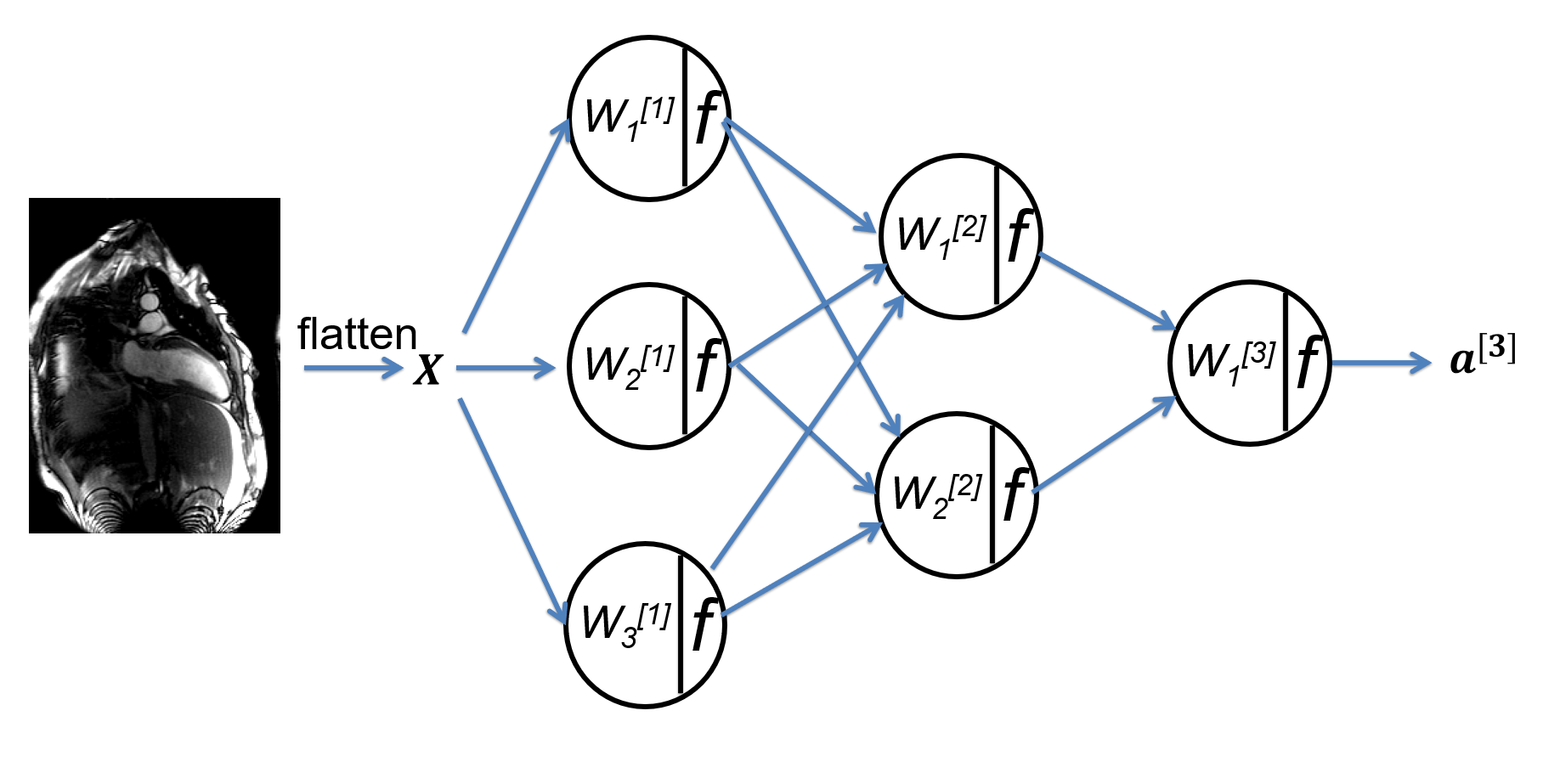
We start by motivating the deep learning for its broad applicability and future growth, and then introduce deep learning as a data driven approach. The basic terminology of neural network are reviewed. We set the stage for future discussion to introduce the binary and multi-class classification problems and the multi-layer perceptron (MLP) network. Other topics covered in this lecture include matrix broadcasting, universal approximation, logits, activation function etc.
Video
Slides
Suggested Reading
The same three authors wrote these two papers at the beginning of DL revolution and now. It is interesting to read and compare them.
Lecture 2
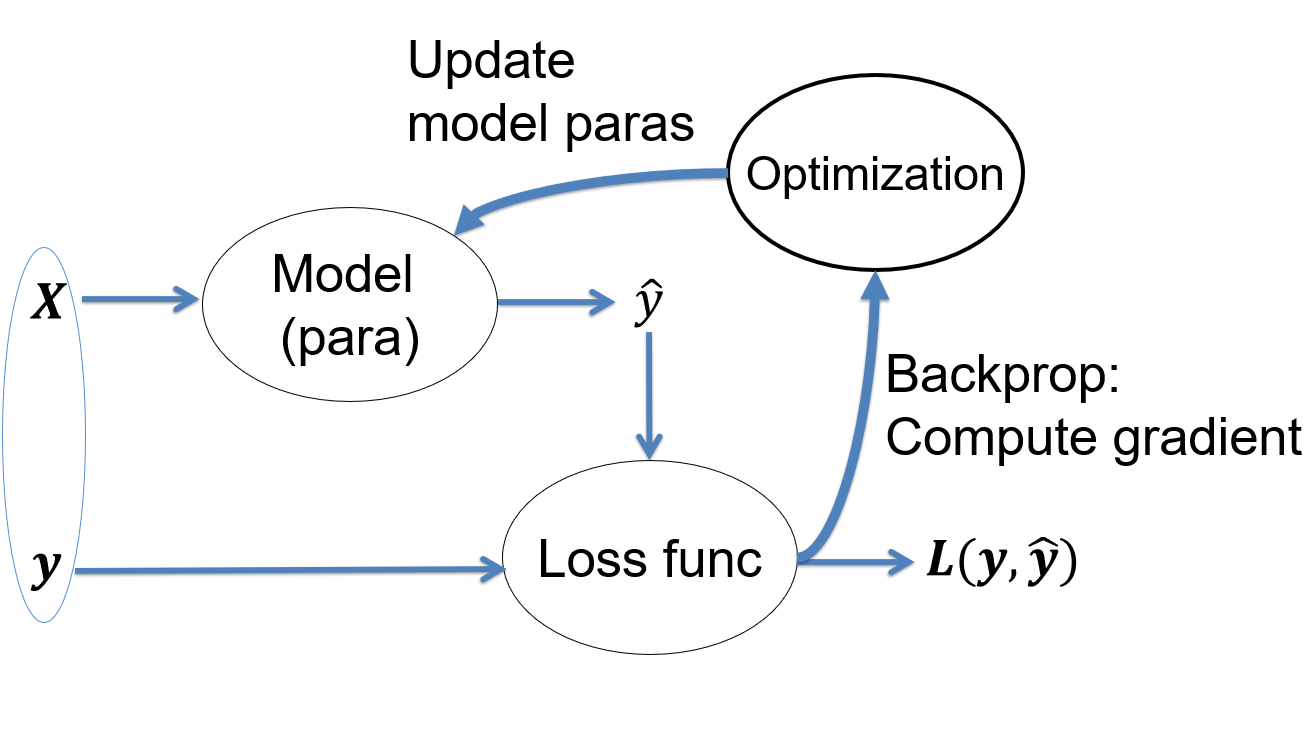
This lecture introduces the concept of loss function to evaluate how well our model fits the data. The process to adjust model parameters to fit the data is called optimization. Gradient descent is a common algorithm used to optimize the model parameters, given the input dataset. This process is the training. We will review different training algorithms and introduce the concepts of training and testing. To measure our model performance in training and testing datasets, the bias and variance of model should be estimated. Other concepts introduced in this lecture include regularization, under-fitting, over-fitting, batch and mini-batch etc.
Video
Slides
Suggested Reading
Lecture 3
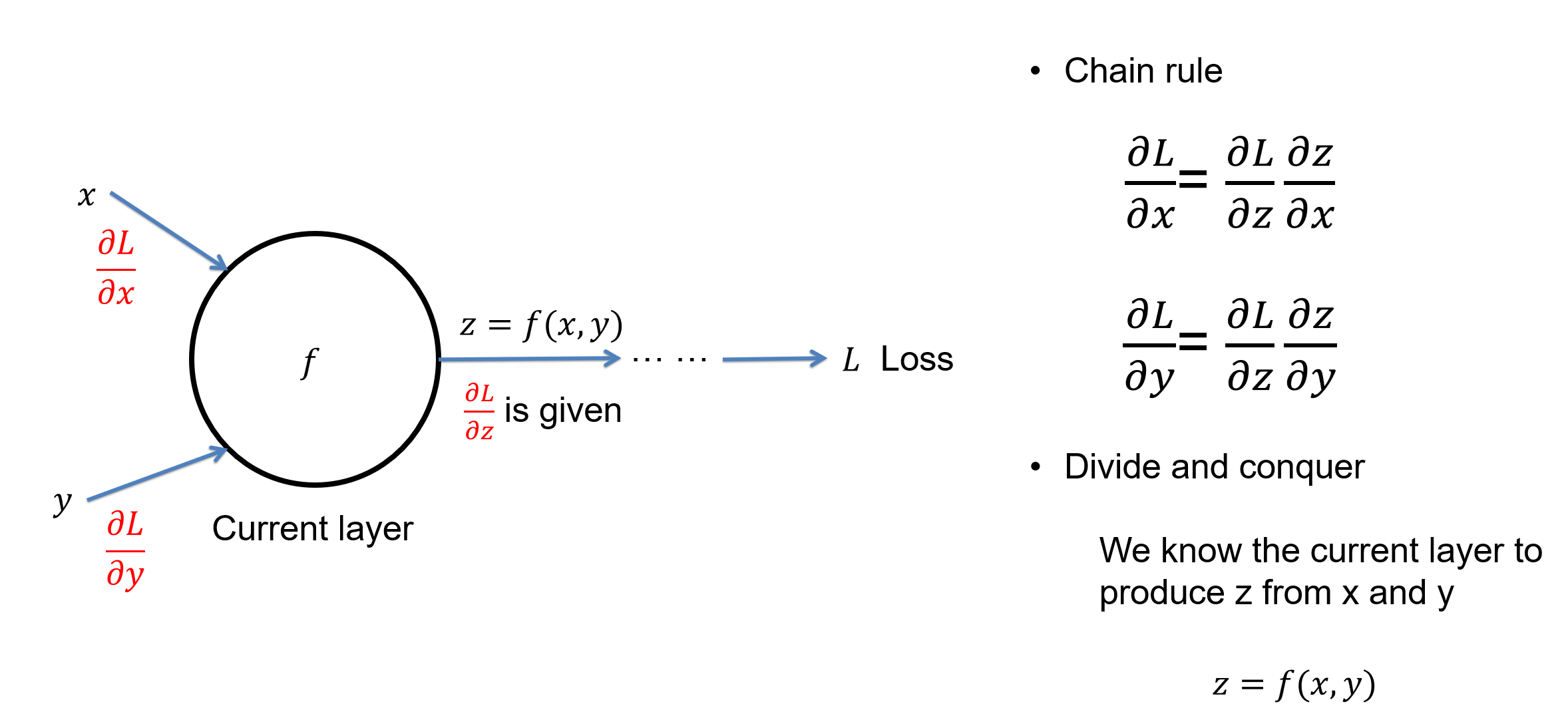
The key step to train a model is to follow the negative gradient direction to reduce the loss. But how do we compute the gradient direction? Through a process called the back propagation or backprop in short. This lecture discusses the backprop in detail. Backprop is based on two ideas: chain rule of derivative and divide-and-conquer. It allows us to compute complex derivative from loss to every learnable parameters in the model.
We will not review GPU devices for deep learning in lectures. Please review two documents in this week's reading list.
Video
Slides
Suggested Reading
Lecture 4
An interactive session to reveal the math behind the neural network
This lecture will review the math behind backprop and gradient update. In particular, we will derive the gradients for a binary and multi-class classification multi-layer perception and explain in details why the algorithm is organized in the particular way. The interactive python coding will be conducted to demo how to build up numerical models and how to debug the implementation.
Video
Slides
Suggested Reading and demos
Download the linear regression demo
Drs. Eric Leifer and James Troendle from the NHLBI drafted this excellent notes about the derivation of loss gradient. Please review. Download the notes for gradient derivation
Assignment 1
In this assignment, you will be asked to implement the multi-layer perceptron model and cross-entropy loss. The coding problem will require the implementation for both forward pass and backprop. The gradient descent is used to train the model for higher classification accuracy. We will not use deep learning framework in this assignment, but will use Python+Numpy combination. The goal is to make sure the thorough understanding of mathematics and numeric technique necessary for a classic neural network. Also, it is to encourage one to get familiar with python coding.
This assignment introduces the regression test for model training and evaluation. The Pytest is used for the regression test purpose.
Lecture 5
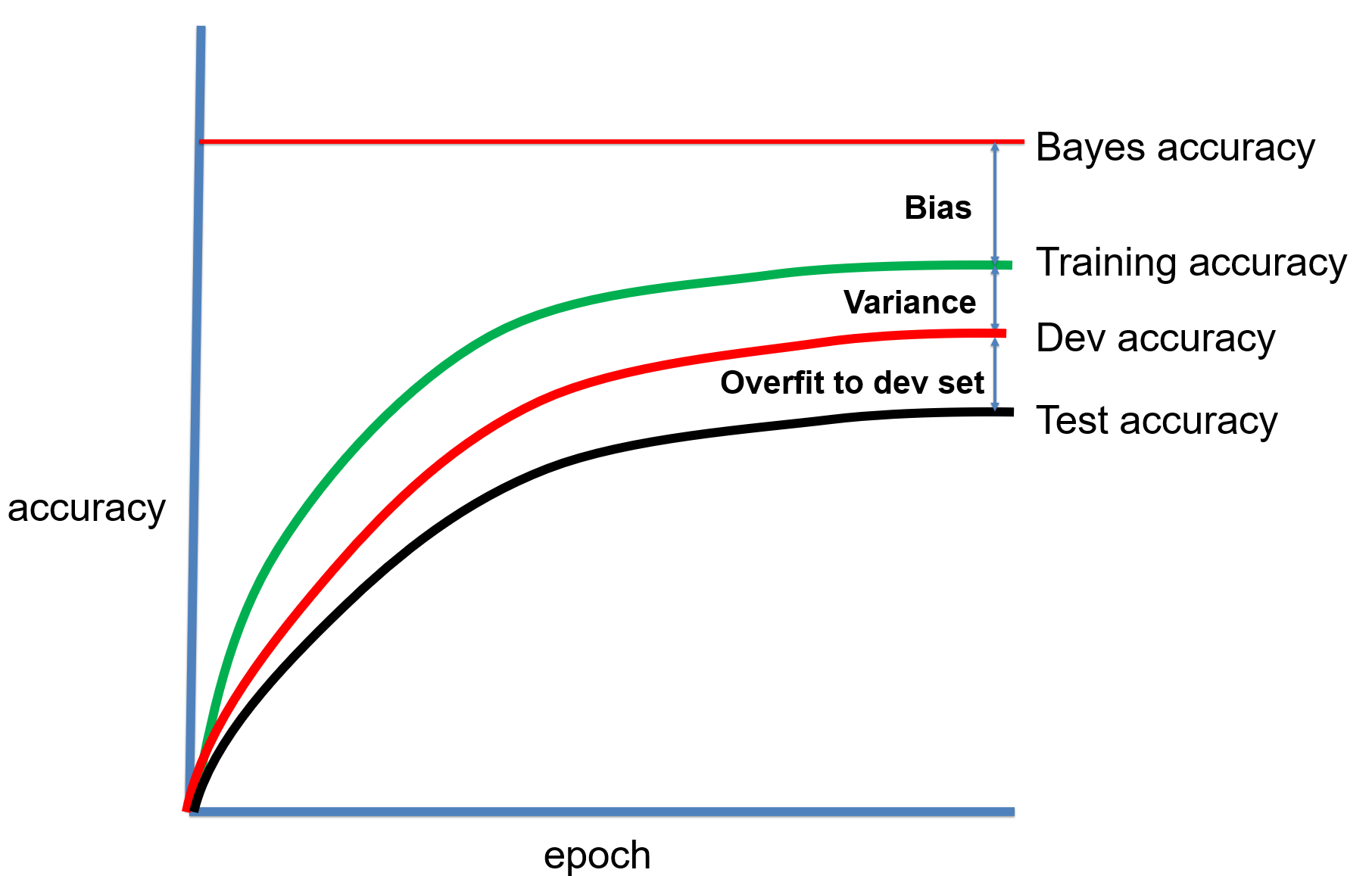
This lecture will finish our discussion on different optimization algorithms. We will introduce a few new methods and compare their pros and cons. The concept of hyper-parameter is explained, where a very important one is the learning rate. Different learning rate scheduling strategies are discussed in this lecture and help boost training performance. To search a good configuration of hyper-parameters, we will discuss coarse-to-fine, hyper-band and Bayesian methods. We close the lecture by discussing bag of tricks to set up the training process and cross-validation.
Video
Slides
Suggested Reading
- Optimization in deep learning
- Learning rate scheduler in Pytorch
- One-cycle learning rate scheduler
- One-cycle learning rate scheduler, post
- Hyper-parameter searching
- Set up training, chapter 40, 41, 42
- DL experiment management
Lecture 6
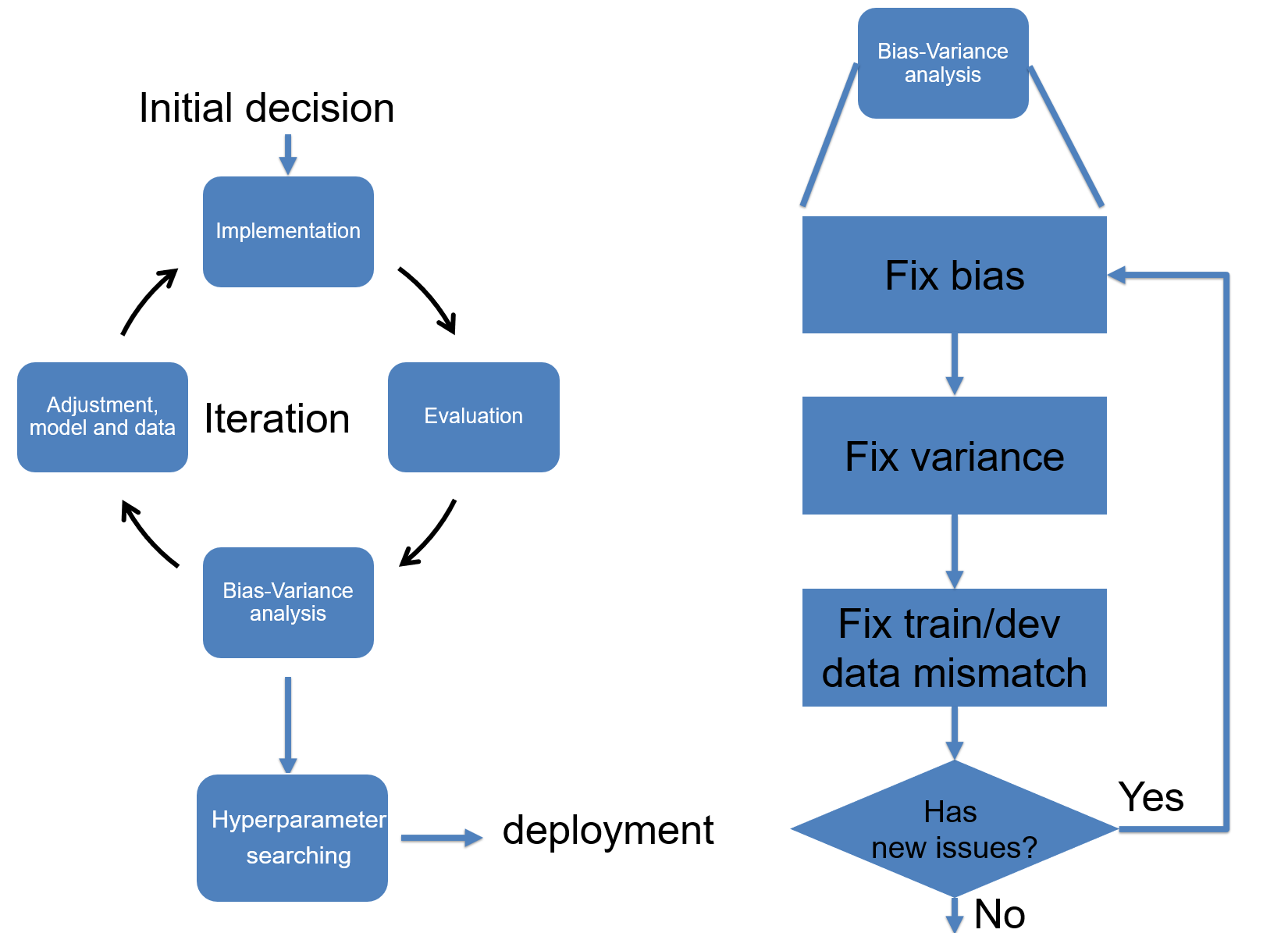
This lecture continues our discussion on training setup, with focus on handling data mismatching between training and test sets. The meaning and strategy to conduct error analysis are introduced. After finishing the training section, we discuss the method for data pre-processing and how to initialize the model parameters. The final section of this lecture introduces the deep learning debugging and iteration for model training. Tools for debugging are demonstrated.
Video
Slides
Suggested Reading
Assignment 2
In this assignment, you will study the autodiff in Pytorch, which is essential to understand how DL models work. Then you will implement a MLP model using Pytorch on the Cifar10 dataset. Another important aspects in this assignment is the experimental management, using the wandb.
Lecture 7
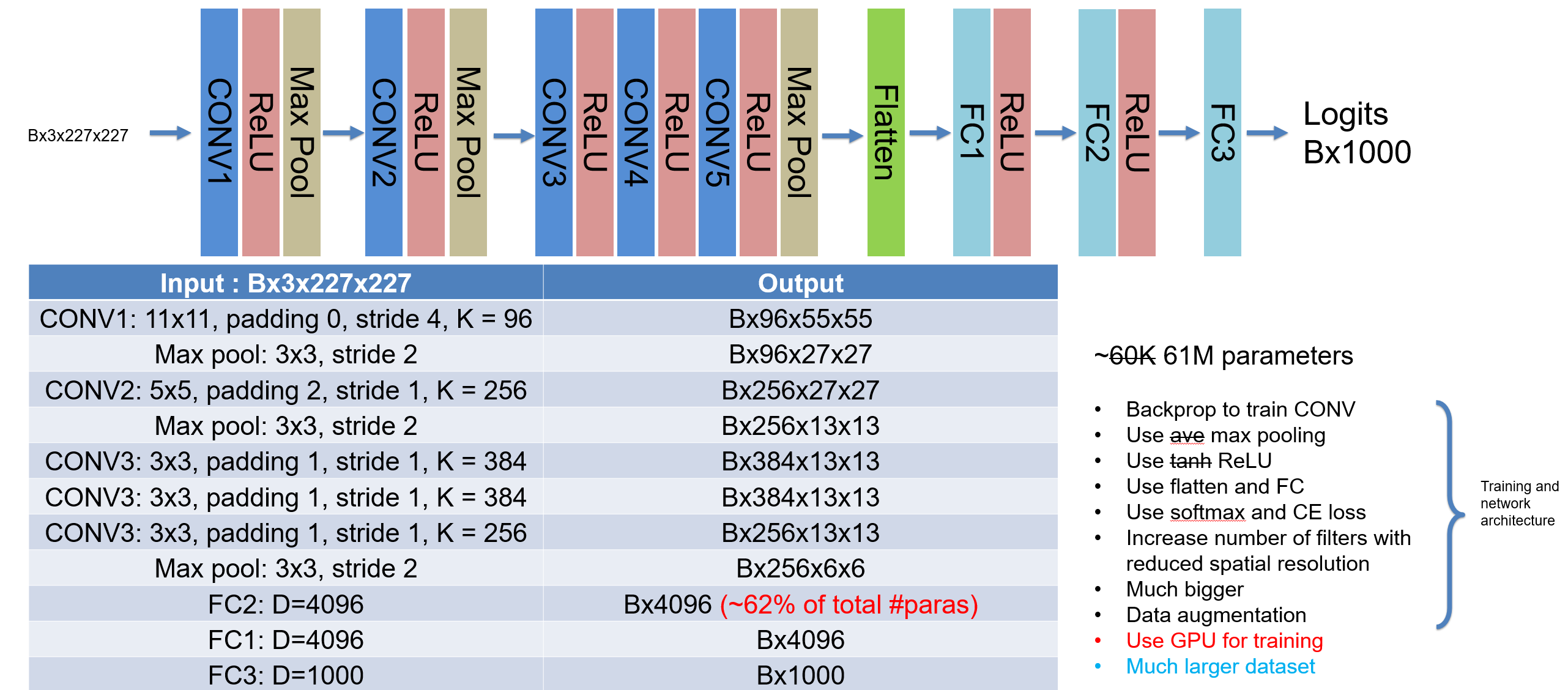
This lecture starts the convolutional neural network (CNN) by introducing the convolution operation and its application on image. Different variants of convolution is discussed, including stride, transpose, dilated CONV, 1D and 3D CONV, padding, and pooling. Image interpolation layer is introduced with other methods to up/downsample images. The batch normalization is discussed with other feature normalization methods. Two CNN architectures are analyzed, LeNet-5 and AlexNet, in the history of ImageNet challenge.
Video
Slides
Suggested Reading
- CONV and its variants
- CNN explanation
- Introduction for batch norm, layer norm, group norm etc.
- Overview of NN feature normalization
- ImageNet Winning CNN Architectures
Lecture 8
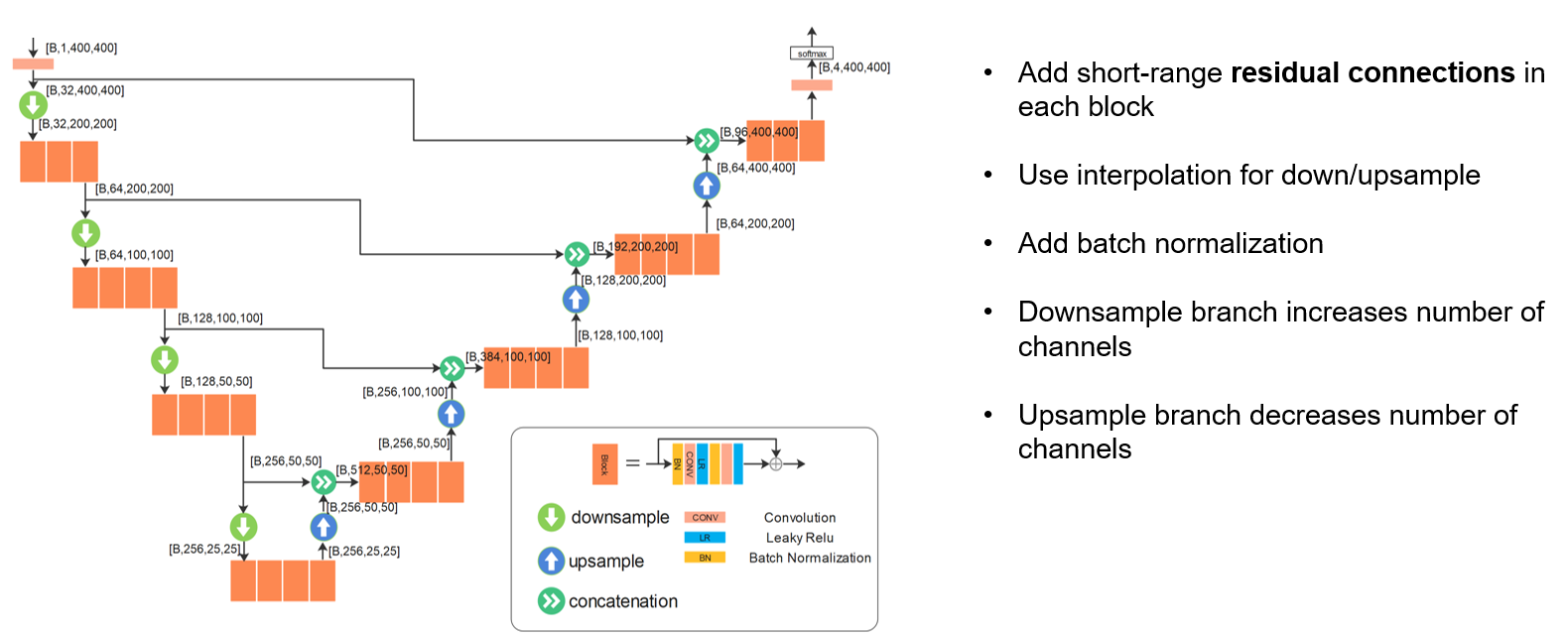
With the basics of CONV and CNN introduced in last lecture, we continue to go through the history of ImageNet competition and reviewed winning architectures until 2017 and go beyond for very latest developments, including ResNet and its variants, group convolution, mobile net, efficient net. We can learn key ideas to design and refine the CNN architectures. The second part of this lecture discusses applications of CNN, including two-stage and one-stage object detection, landmark detection, U-net for segmentation, denoising CNN and super-resolution CNN.
Network compression is not discussed in the lecture. But you are encouraged to read more on this topic.
Video
Slides
Suggested Reading
- ResNet paper
- ResNet with batch norm
- Introduction for batch norm, layer norm, group norm etc.
- Mobile, shuffle, effnet
- One-stage object detector
- ResUnet
- Intro for network compression
Assignment 3
In this assignment, you will practice to build CNN models. Two new datasets are introduced, cifar10 and carvana datasets. You will build classficiation CNN models on cifar10 datasets and build a segmentatin U-net model on carvana datasets. This is an important assignment. Please give a try!